Consolidated expertise
at all 6 locations worldwide
The versatile and universal applicability of thermoplastics provides the basis for our work at all our production sites. In plastic molding, the technologies we use range from compact and multi-component injection molding to precision injection molding, liquid silicone injection molding, MuCell® injection molding and chemical foaming.
We offer application-oriented further processing of the manufactured plastic parts using 1C and 2C PUR foams as well as several plastic welding processes and implement semi-automated and fully automated assembly processes. The high quality of our products is ensured thanks to a wide range of testing technologies.
Injection molding technologies
Compact injection molding with only one component (1C) is a technology for the production of functional plastic parts with precise dimensions in a wide variety of products. Multi-component injection molding (e.g. 2C for two components) can be used to produce plastic parts from different plastics (e.g. hard-soft compounds and in different colors) cost-effectively with just one injection molding machine. The advantage is that there is no need for additional assembly.
Precision injection molding makes it possible to manufacture products in different sizes and with varying accuracy.
Silicones are high-quality materials that acquire their specific properties in a special manufacturing process. Processing takes place on injection molding machines designed for this purpose with a cool cylinder module and hot mold.
The MuCell® technology for injection molding of microcellular foam from thermoplastics offers unique cost saving potentials compared to conventional injection molding. The combination of lower density and cycle time reduction often results in cycle, material and weight savings of over 15%. In terms of quality, MuCell® parts are distinguished by higher dimensional stability than conventionally manufactured parts and, at the same time, eliminate sink marks.
In chemical foaming, a blowing agent is added to the plastic. This chemical additive decomposes by releasing a gas during plastification of the plastic as the temperature rises. Here, too, the gas dissolves while maintaining a minimum pressure in the melt.
PU foams
With single-component polyurethane foaming, there is no need to mix and chemically react the base material with the blowing agent which would otherwise be necessary with 2-component systems. This also dispenses with dosing errors or fluctuations. Even very small quantities can be dosed reliably and reproducibly. In the manufacturing process, the (viscous) liquid material is applied directly to the component as a foam bead.
The reaction of 2C sealing foams is started by mixing the A-component (resin) and B-component (hardener). The result is a chemical reaction with a uniform progression under room temperature conditions. The applied mass foams up to a uniform seal. The seal is foamed directly onto the component.
Plastic welding
Hot gas welding is a patented process used to achieve high-strength, homogeneous and particle-free thermal welding of high-performance plastics.
The hot plate welding process is one of the oldest and most proven joining methods in the plastics industry. It is regarded as a reliable welding process for thermoplastics. Joining surfaces of the molded parts to be welded are adequately heated by means of an electrically heated heating element through contact (heat conduction) and then welded under pressure.
The process of rotary friction welding is well suited for joining rotationally symmetrical shaped parts and has proven to be the ideal joining technique for the production of so-called mass parts. The heat required to plasticize the material is generated by interfacial friction between the two molded parts. The part to be welded on is set in a rotating motion, while the second associated part is firmly fixed.
In ultrasonic welding, the heat required for plasticizing is generated by the conversion of ultrasonic vibrations into mechanical vibrations and is fed to the workpiece to be welded via the sonotrode at a certain contact pressure. Only thermoplastics can be joined with this friction welding process.
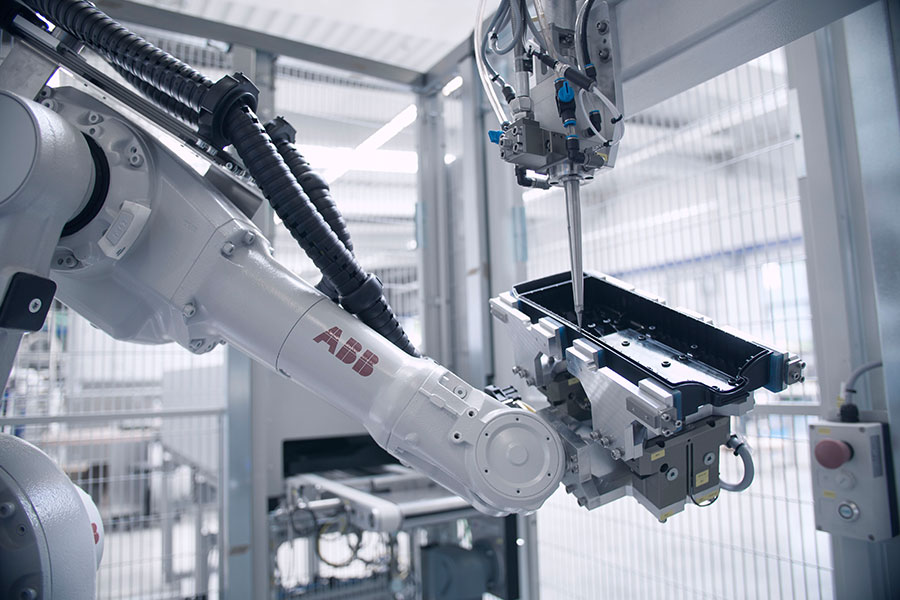
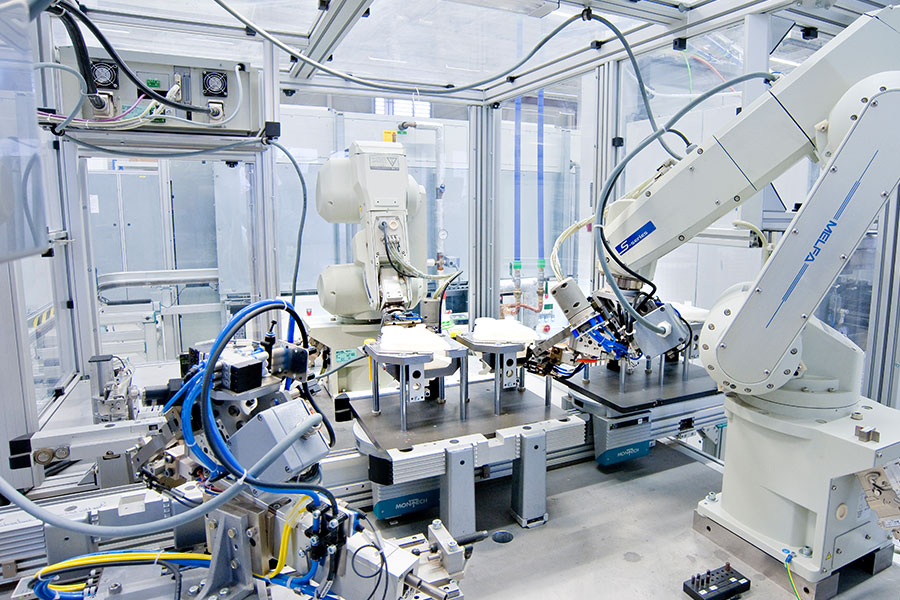
Innovative assembly and testing technologies
Optical inspection using camera systems (e.g. for missing parts or geometries, external dimensions, grid dimensions).
The leakage test is carried out to demonstrate the tightness in vacuum and/or overpressure procedures.
Customer-specific machines and assembly systems for high-precision assembly tasks.
The movement of the holders is centrally controlled in these systems. They are therefore cost-effective. The fixtures are only moved at the positions where this is necessary.
We use assembly lines to carry out semi-automated or fully automated mechanical assembly of large quantities and low cycle times with high repetition accuracy.
Classic manual assembly is only used for small series or prototype production.
Toolmaking
Using state-of-the-art software such as Think and CATIA, we produce complex designs with production-ready parts lists, component drawings and calculations for distortion and air inclusions. The quality of the components is our top priority.
We grind workpieces on state-of-the-art CNC grinding machines based on drawings and CAD data with the very highest degree of precision.
Wire eroding is the key technology of our company. Experienced employees cut filigree contours with highest precision and very high quality from various materials.
We erode filigree contours with the highest precision using state-of-the-art die-sinking systems. The presetting of the workpieces and the graphite electrodes takes place externally on a measuring machine and is then loaded onto the die-sinking machine with automation. Running times of up to 23 hours per day are achieved here.
In CNC milling, we access the data of the tool design and then create the CNC programs. We then mill high-precision workpieces on our 5-axis milling machine with automation.
Experienced employees assemble the parts prefabricated by the machine operators into an injection mold. Accuracy and quality are the key factors.